Unveiling The Secrets Of The Scotia Sea: A Gateway To Understanding Earth’s History And Dynamics
Unveiling the Secrets of the Scotia Sea: A Gateway to Understanding Earth’s History and Dynamics
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Scotia Sea: A Gateway to Understanding Earth’s History and Dynamics
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the Scotia Sea: A Gateway to Understanding Earth’s History and Dynamics. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of the Scotia Sea: A Gateway to Understanding Earth’s History and Dynamics
.png)
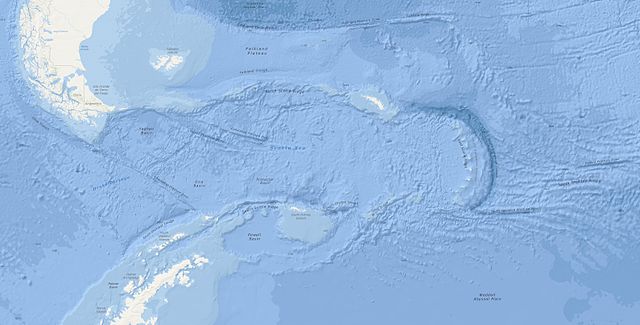
The Scotia Sea, a vast expanse of water separating the southern tip of South America from the Antarctic Peninsula, holds a unique position in the global oceanographic landscape. Its strategic location, coupled with its complex geological history and diverse marine ecosystems, make it a fascinating subject of study for scientists and explorers alike. This article delves into the intricacies of the Scotia Sea, exploring its geological origins, its role in global ocean circulation, and its rich biodiversity.
A Tapestry of Geological Events:
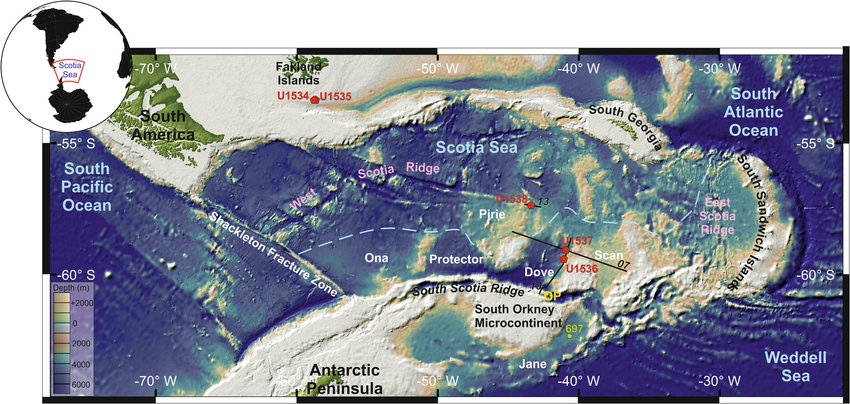
The Scotia Sea’s formation is a testament to the dynamic forces that have shaped our planet. Approximately 65 million years ago, the South American and Antarctic continents were joined together, forming a single landmass. The breakup of this supercontinent, known as Gondwana, led to the opening of the South Atlantic Ocean, a process that continues to this day. The Scotia Sea, a remnant of this ancient geological event, bears the scars of tectonic activity, evidenced by its numerous islands, submerged plateaus, and active volcanic regions.
The most prominent feature of the Scotia Sea is the Scotia Arc, a chain of volcanic islands and seamounts that stretches from the South Sandwich Islands to the South Shetland Islands. This arc, formed by the subduction of the South American Plate beneath the Scotia Plate, is a hotbed of geological activity, with frequent volcanic eruptions and earthquakes. The presence of these features provides valuable insights into the processes of plate tectonics and the evolution of Earth’s crust.
A Vital Link in the Global Ocean Circulation:
The Scotia Sea plays a crucial role in regulating global ocean circulation, acting as a conduit for the exchange of heat, salt, and nutrients between the Atlantic and Southern Oceans. The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC), the largest ocean current in the world, flows through the Scotia Sea, carrying vast amounts of cold, oxygen-rich water from the Southern Ocean towards the Atlantic. This current is a significant driver of global climate patterns, influencing the distribution of heat and precipitation across the globe.
The Scotia Sea also serves as a key location for the formation of Antarctic Bottom Water (AABW), a dense, cold water mass that forms in the Weddell Sea and flows northward along the continental slope, ultimately sinking to the bottom of the Atlantic Ocean. AABW plays a vital role in the global ocean’s thermohaline circulation, a system of interconnected currents that distributes heat and nutrients around the world.
A Biodiversity Hotspot:
Despite its harsh environmental conditions, the Scotia Sea teems with life, hosting a diverse array of marine species. The cold, nutrient-rich waters support a rich ecosystem, including abundant populations of krill, fish, seabirds, seals, and whales. The region is particularly important for breeding and feeding grounds for many species, including the endangered Southern Right Whale and the iconic Adelie penguin.
The Scotia Sea’s biodiversity is a testament to its unique ecological niche. The convergence of warm Atlantic waters and cold Antarctic waters creates a dynamic environment that supports a wide range of marine life. The presence of numerous islands and seamounts further enhances the diversity of the ecosystem, providing a variety of habitats for different species.
Challenges and Conservation:
Despite its ecological importance, the Scotia Sea faces several challenges, including climate change, overfishing, and pollution. Rising ocean temperatures and changes in ocean currents are impacting the distribution and abundance of marine species, particularly those adapted to cold water conditions. Overfishing, particularly of krill, which forms the base of the food chain, poses a serious threat to the ecosystem’s stability. Pollution from land-based sources, such as oil spills and plastic waste, also contaminates the marine environment.
Conservation efforts are crucial to protect the Scotia Sea’s unique biodiversity and ensure its long-term health. International agreements, such as the Convention on the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR), have been established to regulate fishing activities and protect vulnerable species. Research and monitoring programs are also essential to understand the impact of climate change and other threats and develop effective management strategies.
The Scotia Sea: A Window into Earth’s Past and Future:
The Scotia Sea stands as a remarkable example of the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems. Its geological history, oceanographic role, and biodiversity highlight the complex interactions between plate tectonics, climate change, and marine life. Understanding the Scotia Sea’s dynamics is crucial for comprehending the past, present, and future of our planet.
FAQs about the Scotia Sea:
1. What is the Scotia Sea’s significance in terms of global ocean circulation?
The Scotia Sea plays a pivotal role in global ocean circulation, acting as a key conduit for the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, which carries cold, oxygen-rich water from the Southern Ocean towards the Atlantic. It is also a major site for the formation of Antarctic Bottom Water, a dense, cold water mass that contributes to the global thermohaline circulation.
2. What are the main threats to the Scotia Sea’s ecosystem?
The Scotia Sea faces several threats, including climate change, overfishing, and pollution. Rising ocean temperatures, changes in ocean currents, and overexploitation of marine resources pose significant challenges to the ecosystem’s stability and biodiversity.
3. What measures are being taken to protect the Scotia Sea’s biodiversity?
International agreements, such as the Convention on the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR), have been established to regulate fishing activities and protect vulnerable species. Research and monitoring programs are also underway to understand the impact of threats and develop effective management strategies.
4. What is the Scotia Arc, and why is it significant?
The Scotia Arc is a chain of volcanic islands and seamounts that stretches from the South Sandwich Islands to the South Shetland Islands. It is formed by the subduction of the South American Plate beneath the Scotia Plate and is a hotbed of geological activity, providing valuable insights into plate tectonics and the evolution of Earth’s crust.
5. What are some of the unique marine species found in the Scotia Sea?
The Scotia Sea is home to a diverse array of marine species, including abundant populations of krill, fish, seabirds, seals, and whales. It is a crucial breeding and feeding ground for many species, including the endangered Southern Right Whale and the iconic Adelie penguin.
Tips for Further Exploration:
- Visit online resources: Explore websites dedicated to oceanography, marine biology, and Antarctic research to delve deeper into the Scotia Sea’s unique characteristics.
- Read scientific publications: Seek out research papers and articles published in peer-reviewed journals that focus on the Scotia Sea’s geology, oceanography, and biodiversity.
- Engage with experts: Connect with scientists, researchers, and conservationists working in the region to gain insights into current research and conservation efforts.
- Explore documentaries and films: Watch documentaries and films that showcase the Scotia Sea’s stunning landscapes, diverse marine life, and the challenges it faces.
Conclusion:
The Scotia Sea, a gateway to the Southern Ocean, stands as a testament to the dynamic forces that have shaped our planet. Its complex geological history, crucial role in global ocean circulation, and rich biodiversity make it a vital component of Earth’s interconnected systems. Understanding the Scotia Sea’s intricacies is essential for comprehending the past, present, and future of our planet, highlighting the need for continued research, conservation efforts, and responsible stewardship of this vital marine environment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the Scotia Sea: A Gateway to Understanding Earth’s History and Dynamics. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Beyond Distortion: Exploring The World With Non-Mercator Projections
- Navigating The Natural Beauty Of Blydenburgh Park: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Trails
- Navigating The Wilderness: A Comprehensive Guide To Brady Mountain Campground Maps
- Navigating The Road Less Traveled: A Comprehensive Guide To Gas Map Calculators
- Navigating Bangkok: A Comprehensive Guide To The BTS Skytrain
- Navigating Copenhagen: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Train Network
- Unlocking The Secrets Of The Wild West: A Comprehensive Guide To Red Dead Redemption 2’s Arrowhead Locations
- Unveiling The Enchanting Tapestry Of Brittany: A Geographical Exploration
Leave a Reply