Understanding The Seismic Landscape Of North Carolina: A Comprehensive Guide To Fault Lines
Understanding the Seismic Landscape of North Carolina: A Comprehensive Guide to Fault Lines
Related Articles: Understanding the Seismic Landscape of North Carolina: A Comprehensive Guide to Fault Lines
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Seismic Landscape of North Carolina: A Comprehensive Guide to Fault Lines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Seismic Landscape of North Carolina: A Comprehensive Guide to Fault Lines
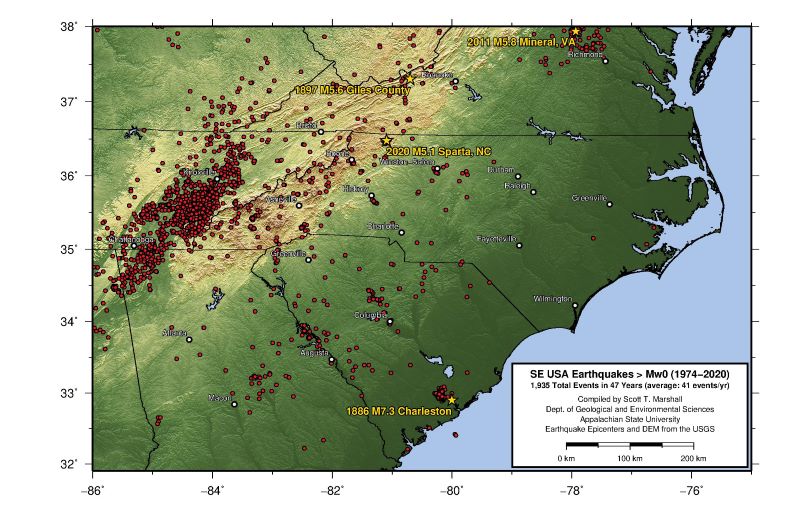
North Carolina, often associated with its picturesque landscapes and vibrant culture, also harbors a geological history marked by seismic activity. While not as prone to catastrophic earthquakes as some other regions, the state is not immune to tremors. Understanding the network of fault lines traversing the state is crucial for appreciating the potential risks and informing responsible planning for infrastructure and development.
Delving into the Fault Lines of North Carolina
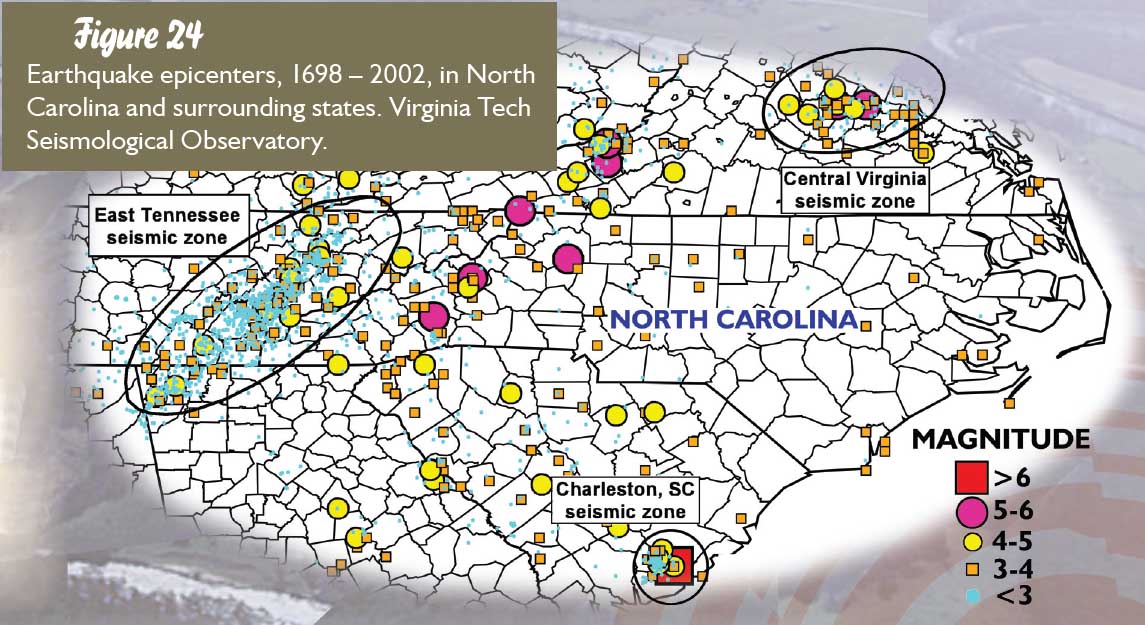
Fault lines represent zones of weakness in the Earth’s crust where tectonic plates move and interact. These movements, though often imperceptible, can generate seismic waves, resulting in earthquakes. North Carolina’s geological history reveals a complex interplay of fault lines, some active and others dormant, each with the potential to impact the state’s seismic landscape.
Mapping the Fault Lines:
Several key fault lines dissect North Carolina, each with its own characteristics and history:
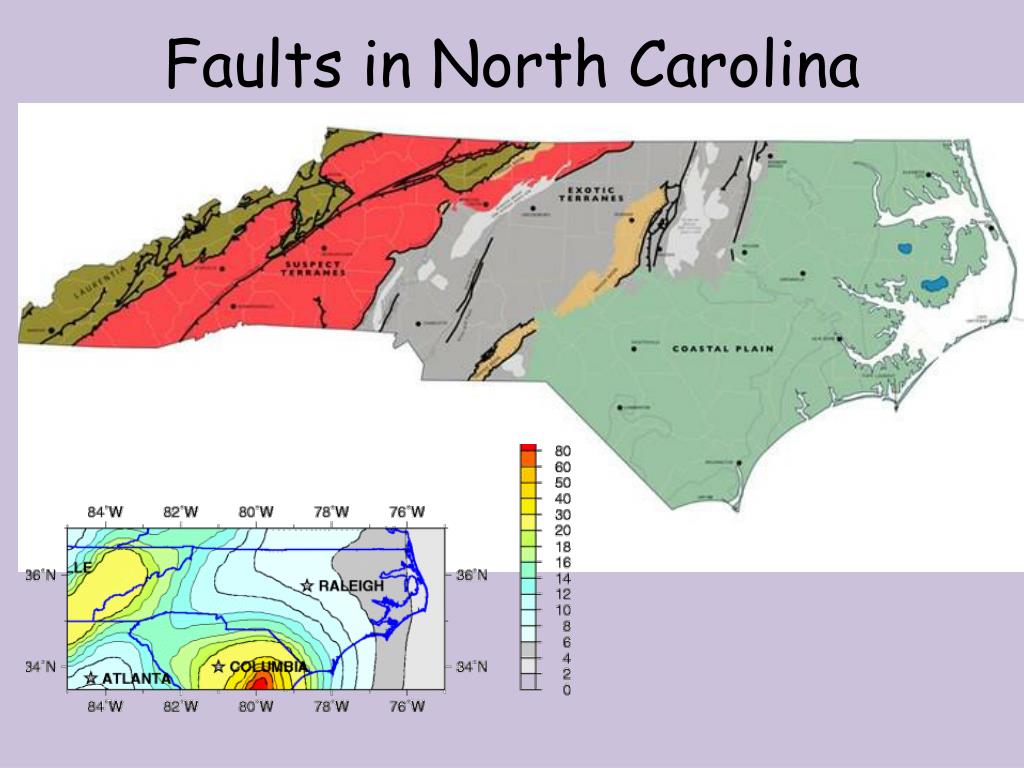
- Brevard Fault Zone: This major fault zone stretches for over 200 miles across western North Carolina, marking the boundary between the Blue Ridge and Piedmont provinces. The Brevard Fault Zone is a complex system of interconnected faults, some of which show evidence of recent movement.
- Eastern Piedmont Fault System: This system comprises a network of faults running roughly parallel to the Fall Line, a geological boundary separating the Piedmont Plateau from the Coastal Plain. While considered less active than the Brevard Fault Zone, the Eastern Piedmont Fault System has been linked to historical earthquakes.
- Central Carolina Fault Zone: This zone, traversing central North Carolina, has been associated with minor earthquakes, particularly in the vicinity of the Uwharrie Mountains.
- Coastal Plain Faults: Several faults are found within the Coastal Plain, extending from the Fall Line to the Atlantic Ocean. These faults are often associated with subtle movements and are less likely to produce significant earthquakes.
Understanding the Importance of Fault Line Mapping
Mapping fault lines is essential for various reasons:
- Seismic Hazard Assessment: By identifying and characterizing fault lines, scientists can assess the potential for earthquakes in specific regions. This information is crucial for developing building codes, infrastructure design, and emergency preparedness plans.
- Resource Exploration: Fault lines often act as pathways for mineral deposits and geothermal resources. Mapping these zones helps guide exploration efforts, potentially leading to the discovery of valuable resources.
- Land Use Planning: Understanding the location and activity of fault lines informs land use planning, ensuring that sensitive areas are not developed in ways that could exacerbate seismic risks.
The Role of Technology in Fault Line Mapping
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the way scientists map and study fault lines:
- Geophysical Surveys: Techniques like seismic reflection profiling and magnetotelluric surveys provide detailed subsurface images, revealing the location and structure of fault zones.
- GPS Monitoring: Global Positioning System (GPS) stations are strategically placed to track subtle movements of the Earth’s crust, providing insights into the activity of fault lines.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and aerial photography help identify surface features associated with fault lines, such as lineaments and topographic changes.
The Impact of Fault Lines on North Carolina
While North Carolina is not known for major earthquakes, the presence of active fault lines necessitates an understanding of the potential risks. Historical records document several earthquakes in the state, some causing minor damage. The most significant earthquake in North Carolina’s history, with a magnitude of 5.1, occurred in 1891 near Asheville.
The Importance of Preparedness
Understanding the potential for seismic activity is essential for preparedness. This involves:
- Building Codes and Regulations: Ensuring that buildings are designed and constructed to withstand earthquakes is crucial for minimizing damage and protecting lives.
- Emergency Response Plans: Developing robust emergency response plans, including evacuation routes and communication protocols, is essential for effectively responding to seismic events.
- Public Education: Raising public awareness about earthquake hazards and preparedness measures can empower individuals to take appropriate actions during seismic events.
FAQs Regarding Fault Lines in North Carolina
Q: How often do earthquakes occur in North Carolina?
A: North Carolina experiences minor earthquakes relatively frequently, but major earthquakes are rare. The state averages about 20 earthquakes per year, most of which are too small to be felt.
Q: Are there any areas in North Carolina that are more prone to earthquakes than others?
A: Western North Carolina, particularly near the Brevard Fault Zone, is considered to have a higher risk of earthquakes than other regions.
Q: What are the potential consequences of a major earthquake in North Carolina?
A: A major earthquake could cause significant damage to buildings, infrastructure, and utilities, leading to power outages, water disruptions, and other disruptions. It could also trigger landslides and other geological hazards.
Q: What should I do if I feel an earthquake?
A: If you feel an earthquake, drop, cover, and hold on. Drop to the ground, take cover under a sturdy object, and hold on until the shaking stops. Stay away from windows and anything that could fall.
Tips for Staying Informed and Prepared
- Stay Updated: Follow the latest information and updates from reliable sources like the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the North Carolina Department of Emergency Management.
- Develop a Family Plan: Discuss potential hazards, evacuation routes, and communication plans with your family.
- Secure Your Home: Secure heavy objects, identify potential hazards, and consider earthquake-resistant modifications to your home.
- Prepare an Emergency Kit: Stock up on essential supplies, including water, food, first-aid kit, and communication devices.
Conclusion
North Carolina’s geological landscape, marked by a network of fault lines, underscores the importance of understanding and mitigating seismic risks. By mapping fault lines, researching their activity, and implementing appropriate preparedness measures, the state can minimize the potential impact of earthquakes, ensuring the safety and well-being of its residents. Recognizing the potential for seismic activity is crucial for responsible planning and development, ensuring a future where North Carolina can thrive amidst its unique geological setting.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Seismic Landscape of North Carolina: A Comprehensive Guide to Fault Lines. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Beyond Distortion: Exploring The World With Non-Mercator Projections
- Navigating The Natural Beauty Of Blydenburgh Park: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Trails
- Navigating The Wilderness: A Comprehensive Guide To Brady Mountain Campground Maps
- Navigating The Road Less Traveled: A Comprehensive Guide To Gas Map Calculators
- Navigating Bangkok: A Comprehensive Guide To The BTS Skytrain
- Navigating Copenhagen: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Train Network
- Unlocking The Secrets Of The Wild West: A Comprehensive Guide To Red Dead Redemption 2’s Arrowhead Locations
- Unveiling The Enchanting Tapestry Of Brittany: A Geographical Exploration
Leave a Reply