Navigating The Celestial Sphere: A Guide To Right Ascension And Declination
Navigating the Celestial Sphere: A Guide to Right Ascension and Declination
Related Articles: Navigating the Celestial Sphere: A Guide to Right Ascension and Declination
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Celestial Sphere: A Guide to Right Ascension and Declination. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Celestial Sphere: A Guide to Right Ascension and Declination

The vast expanse of the night sky, with its countless stars and celestial bodies, can seem daunting at first glance. However, just as we use latitude and longitude to pinpoint locations on Earth, astronomers employ a similar system to map the celestial sphere: right ascension and declination. This coordinate system provides a precise and standardized method for identifying the position of any celestial object, allowing astronomers and stargazers alike to navigate the cosmos with ease.
Understanding Right Ascension and Declination
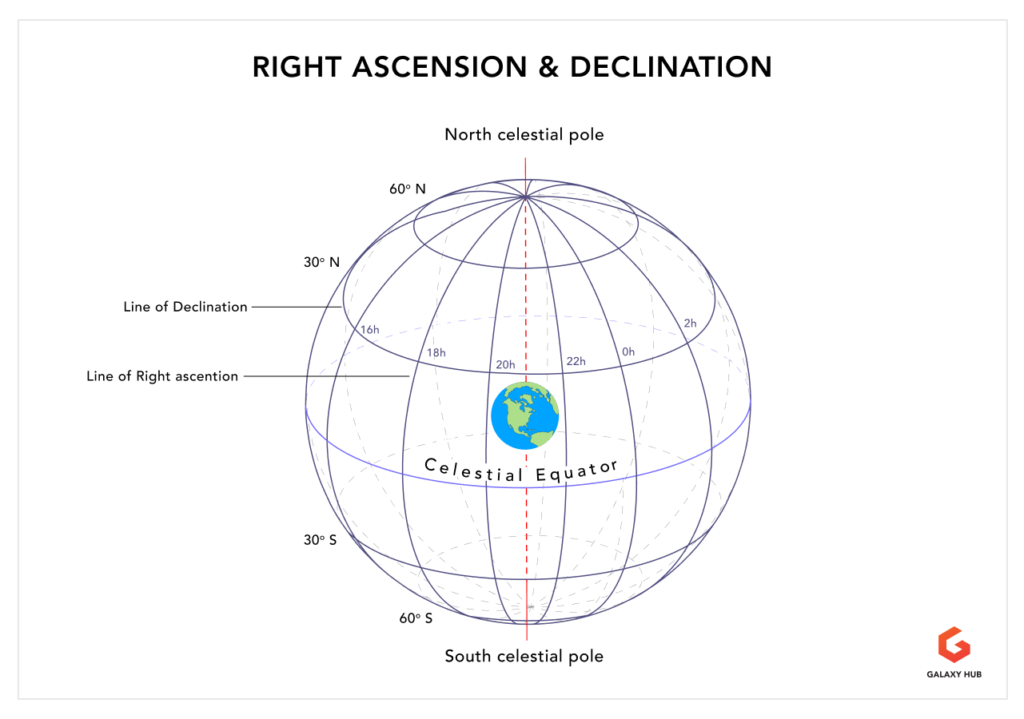
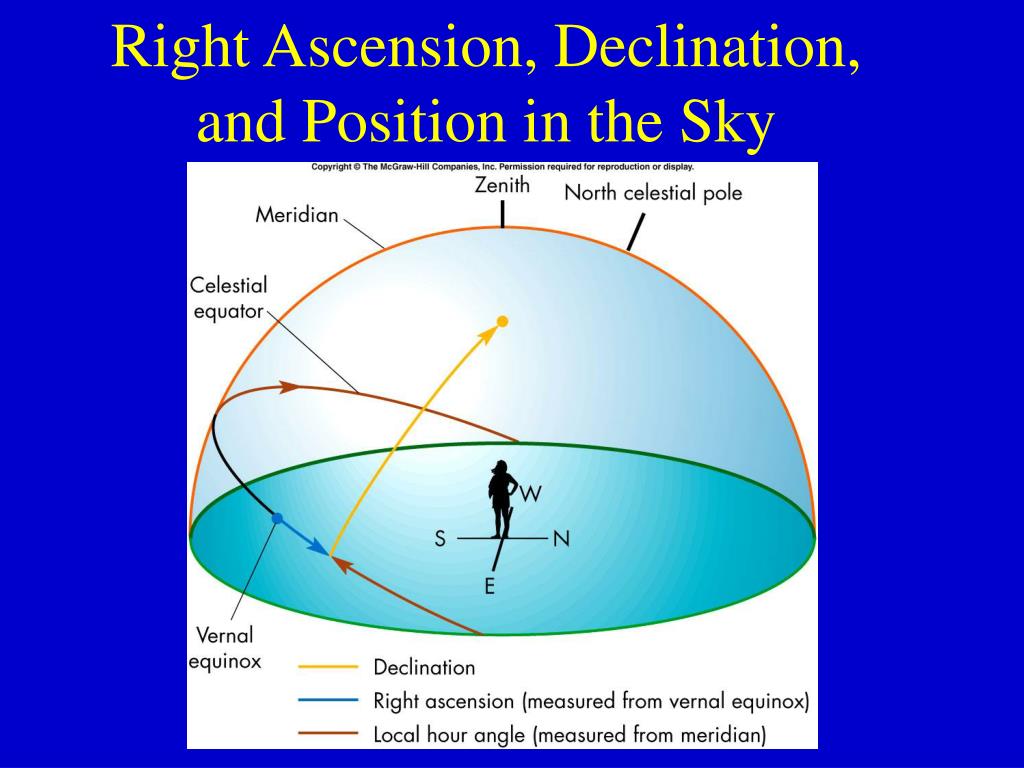
Imagine a giant, celestial sphere encompassing the Earth. This sphere, with the Earth at its center, serves as a framework for mapping the positions of stars and other celestial objects. Right ascension and declination work together to define a specific point on this sphere, analogous to latitude and longitude on Earth.
-
Right Ascension (RA): Similar to longitude, right ascension measures the angular distance of a celestial object eastward along the celestial equator, starting from the vernal equinox. The vernal equinox, also known as the first point of Aries, marks the point where the Sun crosses the celestial equator moving northward. Right ascension is measured in hours, minutes, and seconds, with 24 hours representing a full circle.
-
Declination (Dec): Comparable to latitude, declination measures the angular distance of a celestial object north or south of the celestial equator. It is measured in degrees, ranging from -90° (south celestial pole) to +90° (north celestial pole). A declination of 0° indicates the object lies on the celestial equator.
Visualizing Right Ascension and Declination
To visualize this system, imagine a grid superimposed on the celestial sphere. The celestial equator forms the horizontal axis, while lines of right ascension, running parallel to the equator, form the vertical axis. Declination lines, running perpendicular to the equator, mark the angular distance from the celestial equator. The intersection of a specific right ascension line and declination line pinpoints the exact location of a celestial object.
Benefits of Using Right Ascension and Declination
The right ascension and declination system offers several advantages in astronomical studies:
-
Precise Object Identification: This system provides a standardized and unambiguous method for identifying celestial objects, allowing astronomers to easily locate and track their movement.
-
Simplified Data Sharing: Astronomers worldwide can readily exchange data and information about celestial objects using this common coordinate system.
-
Accurate Object Tracking: Right ascension and declination allow for precise tracking of celestial objects’ movement across the sky, facilitating the study of their orbits and other properties.
-
Predictive Capabilities: By knowing the right ascension and declination of a celestial object, astronomers can predict its future position in the sky, enabling planning for observations and research.
Applications of Right Ascension and Declination
The right ascension and declination system finds wide applications in various astronomical endeavors:
-
Telescope Positioning: Astronomers use this system to accurately point telescopes at specific celestial objects for observation.
-
Satellite Tracking: Right ascension and declination are crucial for tracking satellites and space debris, ensuring safe navigation in space.
-
Astrometric Studies: Astronomers use this system to study the positions and movements of stars and other celestial objects, contributing to our understanding of the universe’s structure and evolution.
-
Star Charts and Celestial Navigation: This system forms the basis for star charts and celestial navigation, allowing astronomers and stargazers to navigate the night sky and locate specific celestial objects.
FAQs on Right Ascension and Declination
1. How does right ascension relate to time?
Right ascension is directly linked to time due to the Earth’s rotation. As the Earth rotates, the celestial sphere appears to rotate in the opposite direction. One full rotation of the Earth takes 24 hours, which corresponds to 360 degrees. Therefore, each hour of right ascension represents 15 degrees of arc on the celestial sphere.
2. Why is the vernal equinox used as the starting point for right ascension?
The vernal equinox is chosen as the starting point for right ascension because it marks the point where the Sun crosses the celestial equator moving northward. This event signifies the beginning of spring in the Northern Hemisphere and is a significant point in Earth’s annual cycle.
3. How do I find the right ascension and declination of a celestial object?
You can use online star charts, astronomical software, or specialized apps to find the right ascension and declination of a celestial object. These resources often allow you to input the object’s name or coordinates and provide its corresponding right ascension and declination.
4. Can right ascension and declination change over time?
While right ascension and declination are typically considered fixed for a specific object, they can change slightly over time due to the precession of the Earth’s axis. Precession is a slow wobble in the Earth’s axis of rotation, causing the celestial poles and the vernal equinox to shift over long periods.
Tips for Using Right Ascension and Declination
-
Use a Star Chart or Planetarium App: These resources provide a visual representation of the celestial sphere, showing the positions of celestial objects based on their right ascension and declination.
-
Familiarize Yourself with the Celestial Equator: Understanding the celestial equator as the reference point for declination is essential for navigating the sky.
-
Practice Identifying Key Constellations: Learning to recognize prominent constellations can help you orient yourself and find specific celestial objects based on their right ascension and declination.
-
Consider Using a Telescope: A telescope allows you to magnify distant objects, enhancing your ability to observe and study celestial objects based on their right ascension and declination coordinates.
Conclusion
Right ascension and declination provide a fundamental framework for mapping and understanding the celestial sphere. This system allows astronomers to precisely locate, track, and study celestial objects, contributing to our understanding of the universe’s vastness and complexity. By mastering this coordinate system, stargazers and amateur astronomers can navigate the night sky with confidence, unlocking the wonders of the cosmos. As our understanding of the universe continues to expand, the right ascension and declination system will remain an indispensable tool for exploration and discovery.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Celestial Sphere: A Guide to Right Ascension and Declination. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Beyond Distortion: Exploring The World With Non-Mercator Projections
- Navigating The Natural Beauty Of Blydenburgh Park: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Trails
- Navigating The Wilderness: A Comprehensive Guide To Brady Mountain Campground Maps
- Navigating The Road Less Traveled: A Comprehensive Guide To Gas Map Calculators
- Navigating Bangkok: A Comprehensive Guide To The BTS Skytrain
- Navigating Copenhagen: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Train Network
- Unlocking The Secrets Of The Wild West: A Comprehensive Guide To Red Dead Redemption 2’s Arrowhead Locations
- Unveiling The Enchanting Tapestry Of Brittany: A Geographical Exploration
Leave a Reply