Deciphering The Language Of Land: A Comprehensive Guide To Reading Survey Maps
Deciphering the Language of Land: A Comprehensive Guide to Reading Survey Maps
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Land: A Comprehensive Guide to Reading Survey Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Land: A Comprehensive Guide to Reading Survey Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of Land: A Comprehensive Guide to Reading Survey Maps

Survey maps, often referred to as land surveys or property surveys, serve as a visual blueprint of a specific parcel of land. They are a crucial tool for various purposes, including property transactions, construction projects, legal disputes, and even historical research. Understanding the intricacies of a survey map empowers individuals to navigate the complexities of land ownership, make informed decisions, and ensure legal compliance.
This comprehensive guide delves into the essential elements of a survey map, providing a clear and informative explanation of its components and their significance.
The Foundation of a Survey Map: Understanding the Basics
At its core, a survey map is a scaled representation of a property’s boundaries, features, and topography. It utilizes specific symbols, lines, and annotations to convey information about the land in a concise and standardized manner. Key elements of a survey map include:
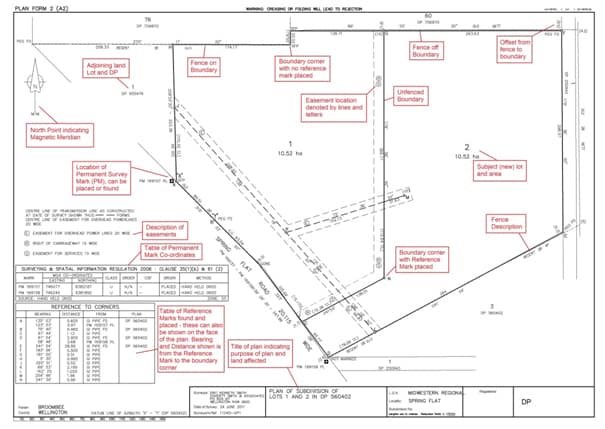
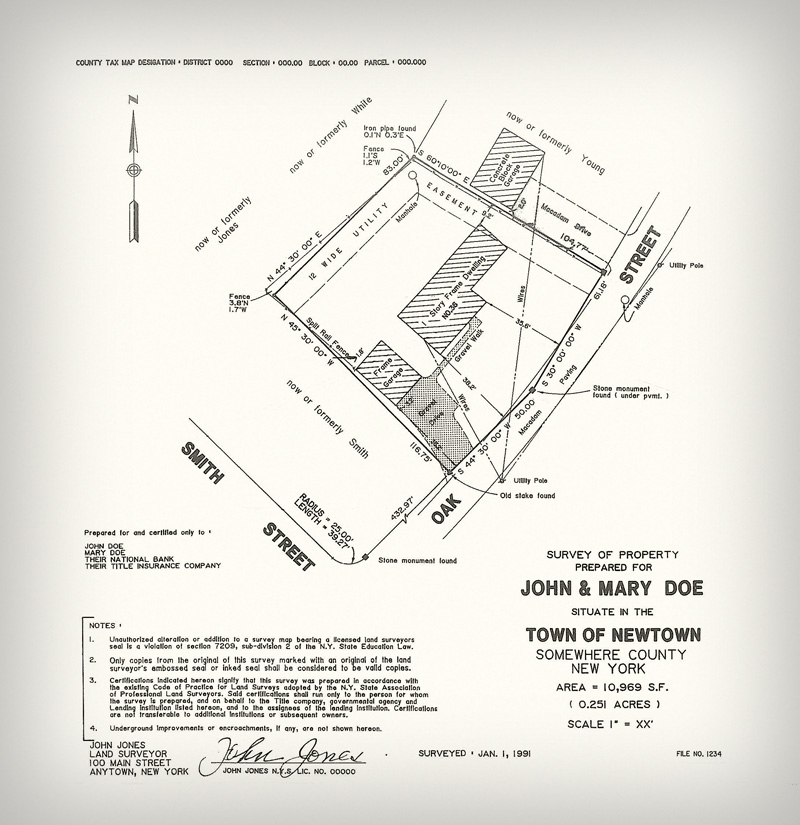
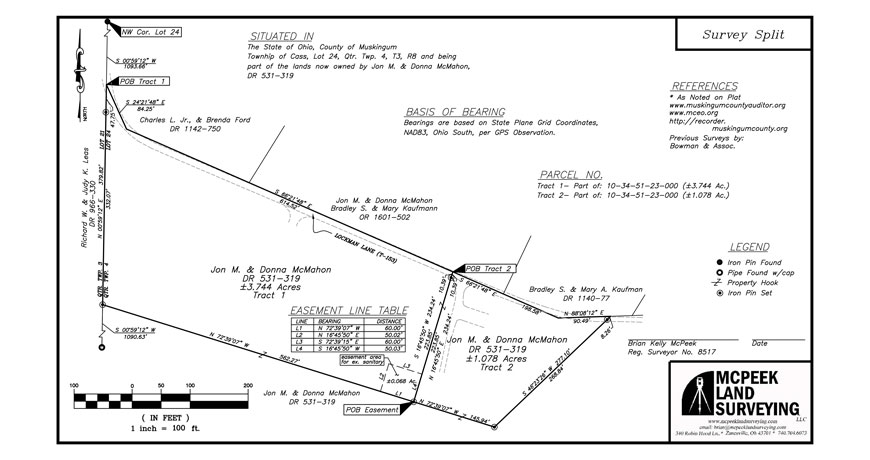
1. The Property Boundary: This is the most fundamental aspect of the map, defining the legal limits of the property. It is typically represented by a thick solid line, often referred to as the "property line." The boundary line encompasses all areas within the property’s ownership, including buildings, structures, and landscaping.
2. Bearings and Distances: These elements provide precise measurements of the property’s dimensions and angles. Bearings indicate the direction of a line relative to North, while distances specify the length of each line segment. These measurements are crucial for accurate calculations of property area and legal descriptions.
3. Survey Monuments: These are permanent markers placed on the ground to denote specific points along the property boundary. They can be various materials, such as concrete posts, iron pipes, or even natural features like trees. Survey monuments serve as physical references for locating property lines and ensuring their long-term accuracy.
4. Topographical Features: These elements represent the natural and man-made features within the property. Contours lines illustrate the elevation changes across the land, while symbols denote specific features like trees, water bodies, and structures. This information is vital for understanding the terrain, potential drainage patterns, and suitability for various uses.
5. Legal Descriptions: Survey maps often include legal descriptions of the property, which are formal descriptions of the land’s boundaries and location. These descriptions are essential for legal documentation, property transactions, and resolving any boundary disputes.
6. Survey Notes and Annotations: These elements provide additional information about the survey, including the date of the survey, the surveyor’s name and license number, and any relevant notes or observations. They can also include details about the survey methodology, potential limitations, and any specific conditions related to the property.
Interpreting the Visual Language: Reading a Survey Map Effectively
To effectively read and interpret a survey map, it is crucial to understand the specific symbols and conventions used in its creation. This requires a combination of visual analysis, spatial reasoning, and knowledge of surveying principles.
1. Understanding the Scale: The scale of a survey map indicates the ratio between the map’s dimensions and the actual dimensions of the property. For example, a scale of 1:100 means that one unit on the map represents 100 units in reality. Understanding the scale is crucial for accurately measuring distances and areas on the map.
2. Deciphering Symbols and Conventions: Survey maps employ specific symbols to represent various features, including:
- Property Lines: Typically shown as solid lines, often with different thicknesses to distinguish between different types of boundaries.
- Easements: Areas granted to others for specific purposes, such as utility lines or access rights.
- Structures: Buildings, fences, and other structures are represented by specific symbols.
- Trees: Trees are often depicted with a small circle or triangle.
- Water Bodies: Rivers, lakes, and streams are shown with blue lines or symbols.
- Contours: Lines connecting points of equal elevation, indicating the slope and topography of the land.
3. Analyzing the Data: Once you have familiarized yourself with the symbols and conventions, you can begin analyzing the data presented on the map. This includes:
- Determining Property Boundaries: Carefully trace the property lines and identify any easements or shared boundaries.
- Measuring Distances and Areas: Use the map’s scale to calculate distances between points and the overall area of the property.
- Identifying Topographical Features: Analyze the contour lines and symbols to understand the land’s elevation changes and potential drainage patterns.
- Evaluating Potential Issues: Look for any inconsistencies or anomalies in the map, such as conflicting boundary lines or discrepancies in measurements.
The Importance of Survey Maps: Unveiling the Benefits
Survey maps play a crucial role in various aspects of land management and ownership. Their benefits include:
1. Establishing Clear Boundaries: Survey maps provide a definitive representation of property boundaries, minimizing the risk of disputes and ensuring legal compliance.
2. Facilitating Property Transactions: Survey maps are essential for property transactions, enabling buyers and sellers to accurately assess the size, shape, and features of the land. They also help identify any potential encumbrances or easements that may affect the property’s use.
3. Guiding Construction Projects: Survey maps are vital for planning and executing construction projects. They provide accurate information about the terrain, existing structures, and utility lines, ensuring efficient and safe construction.
4. Resolving Boundary Disputes: Survey maps serve as legal evidence in boundary disputes, providing objective documentation of property lines and resolving disagreements.
5. Historical Research: Survey maps offer valuable insights into the historical development of land use and ownership patterns. They can reveal information about past settlements, infrastructure, and land divisions.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About Survey Maps
Q: How often should a property be surveyed?
A: The frequency of surveys depends on various factors, including the age of the property, the presence of any recent construction or changes, and the potential for boundary disputes. In general, it is advisable to have a survey conducted at least once every 10-15 years, or whenever there are significant changes to the property.
Q: What are the different types of surveys?
A: There are several types of surveys, each serving a specific purpose. Some common types include:
- Boundary Survey: Defines the legal boundaries of a property.
- Topographic Survey: Maps the elevation changes and features of the land.
- Construction Survey: Provides accurate measurements and data for construction projects.
- As-Built Survey: Documents the final construction details of a project.
Q: Who can conduct a survey?
A: Surveys are typically conducted by licensed professional surveyors. These individuals have undergone specialized training and are certified to perform accurate and legally valid surveys.
Q: Where can I obtain a survey map?
A: Survey maps can be obtained from various sources, including:
- Property Records: Local government offices maintain records of property surveys.
- Real Estate Agents: Real estate agents often have access to survey maps for properties they are listing.
- Professional Surveyors: Licensed surveyors can conduct new surveys or provide copies of existing surveys.
Tips for Reading Survey Maps Effectively
1. Start with the Basics: Begin by understanding the map’s scale, symbols, and conventions. Familiarize yourself with the property’s legal description and any relevant notes or annotations.
2. Analyze the Boundary Lines: Carefully trace the property lines and identify any easements or shared boundaries. Note any potential discrepancies or inconsistencies.
3. Interpret Topographical Features: Study the contour lines and symbols to understand the land’s elevation changes and potential drainage patterns.
4. Seek Professional Guidance: If you encounter difficulties understanding a survey map, consult a licensed surveyor or other qualified professional. They can provide expert interpretation and guidance.
Conclusion: Empowering Understanding through Survey Maps
Survey maps are powerful tools that provide a visual and comprehensive representation of a property’s boundaries, features, and topography. By understanding the elements of a survey map, individuals can gain valuable insights into land ownership, make informed decisions, and navigate the complexities of property management. Whether for legal purposes, construction projects, or simply understanding the land they own, survey maps offer a wealth of information and empower individuals to make informed decisions about their property.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Land: A Comprehensive Guide to Reading Survey Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Beyond Distortion: Exploring The World With Non-Mercator Projections
- Navigating The Natural Beauty Of Blydenburgh Park: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Trails
- Navigating The Wilderness: A Comprehensive Guide To Brady Mountain Campground Maps
- Navigating The Road Less Traveled: A Comprehensive Guide To Gas Map Calculators
- Navigating Bangkok: A Comprehensive Guide To The BTS Skytrain
- Navigating Copenhagen: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Train Network
- Unlocking The Secrets Of The Wild West: A Comprehensive Guide To Red Dead Redemption 2’s Arrowhead Locations
- Unveiling The Enchanting Tapestry Of Brittany: A Geographical Exploration

Leave a Reply